Outdoor Temperature and Water Temperature
Adapting the hot water heating temperature to outdoor temperature allows modulating valves to operate in their design range.
A hot water heating system is in general designed for a maximum heat load at a minimum design outdoor temperature. The outdoor design temperature used depends on national codes, standards and meteorological data valid for the actual locations.
It is common to use an outdoor design temperature that is the statistically lowest temperature for a given period (commonly used are periods of 3 days or similar). Most of the time the outdoor temperature will be significant higher – with an heat load significant lower – than the maximum design heat load.
Therefore, most of the year the heat emission from the radiators and heating elements must be reduced by lowering the mean surface temperature of the heating elements by
reducing the water flow through the radiators, or
reducing the water temperature to the radiators, or
both reducing flow and reducing temperature through/to the radiators
Keeping the hot water design temperature constant through the heating season makes the modulating control valves on the heating elements to perform mostly outside their design range. Modulating valves do not perform very well with reduced flow at nearly closed positions.
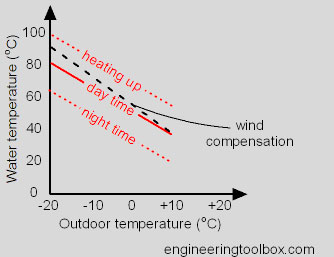
By reducing the water temperature at higher outdoor temperatures as shown in the diagram above, the modulating valves will operate in their design range with much better performance

 Canada
Canada